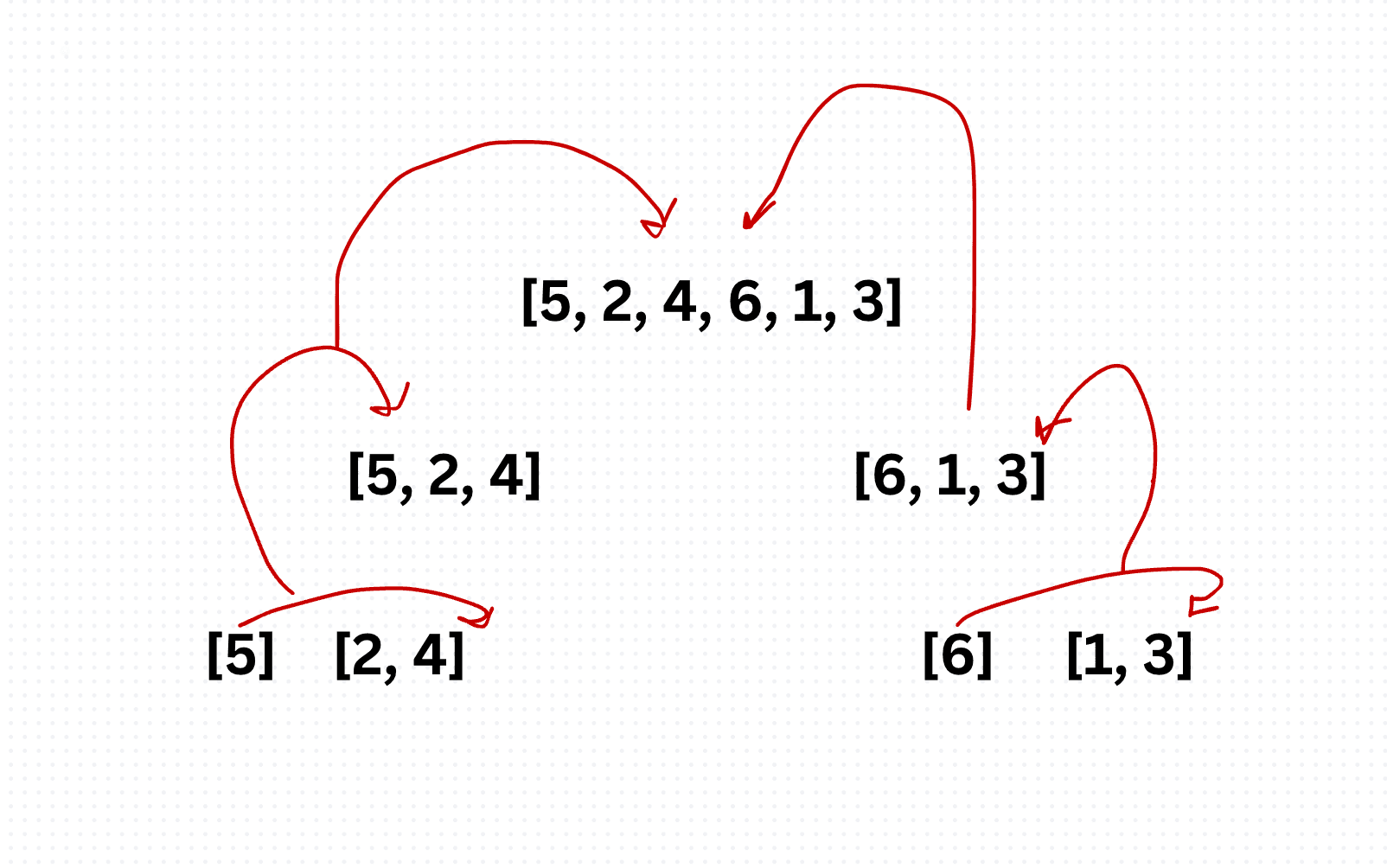
Merge Sort Algorithm
Merge sort operates by recursively dividing the input array into halves until each subarray contains only one element. Then, it merges adjacent subarrays in a sorted manner until the entire array is sorted. The merging process compares elements from each subarray and places them in the correct order.
function mergeSort(arr) {
if (arr.length <= 1) {
return arr;
}
const middle = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
const left = arr.slice(0, middle);
const right = arr.slice(middle);
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right));
}
function merge(left, right) {
let result = [];
let leftIndex = 0;
let rightIndex = 0;
while (leftIndex < left.length && rightIndex < right.length) {
if (left[leftIndex] < right[rightIndex]) {
result.push(left[leftIndex]);
leftIndex++;
} else {
result.push(right[rightIndex]);
rightIndex++;
}
}
return result.concat(left.slice(leftIndex)).concat(right.slice(rightIndex));
}
// Example usage:
const array = [5, 2, 4, 6, 1, 3];
console.log("Original Array:", array);
const sortedArray = mergeSort(array);
console.log("Sorted Array:", sortedArray);Merge sort has a guaranteed time complexity of O(n log n) for all cases, making it one of the most efficient comparison-based sorting algorithms available. This efficiency stems from its divide-and-conquer approach, which ensures that the array is halved logarithmically.
Merge sort's stability and efficiency make it well-suited for various real-world applications, such as sorting large datasets in databases, implementing sorting functionality in programming libraries, and organizing records in web applications.
Merge sort is a powerful sorting algorithm renowned for its stability, efficiency, and guaranteed O(n log n) time complexity.